Operations for Incontinence
Office Urodynamic studies are first offered to a patient who complains of urinary leakage or urinary incontinence.
Overview
Office Urodynamic studies are first offered to a patient who complains of urinary leakage or urinary incontinence. These studies have become indispensable to determine the need for surgery and in some situations to choose the surgical procedure.
We offer
- Office Urodynamics Test.
- Laparoscopic correction of urinary incontinence - Burch operation.
- Vaginal repair of incontinence.
- Vaginal insertion of slings - TVT and TOT sling.
What is a urodynamic test?
It is simply a combination of several useful tests that provide information about your lower urinary tract (bladder and urethra). Urodynamics “draws a picture” of what happens when your bladder fills up and when it empties by measuring volumes and pressures. During the test, you will be catheterized at least once, and your bladder will be filled one or more times with water. Muscle activity in your pelvis will be recorded during the tests by small electrodes connected to a special computer.
Why do you need a Urodynamic study?
A urodynamic study may be recommended if you have problems with storing or passing urine, especially urinary incontinence (leakage of urine) and your doctor needs to evaluate these problems further.
The common indication for study in women with incontinence are:
- As a preoperative assessment.
- Mixed stress-urge symptoms.
- Associated voding problems.
- Mismatch between synptoms and clinical findings.
- Patients with vaginal prolapse requiring repair.
- After previous failed incontinence surgery.
Non-surgical Treatment of Urinary Incontinence
While surgery has a high success rate, it is not always the first line of treatment. Less invasive treatments, like the following, may improve symptoms avoiding the need for surgery:
- Pelvic floor muscle rehabilitation/ Physiotherapy.
- Bladder training.
- Vaginal support devices.
- Medical treatment.
- Obstructive devices.
The input of a Physiotherapist with training on bladder problems is very important for obtaining a reasonable improvement.
Surgical Treatment of Urinary Incontinence
Anterior Repair
A bladder prolapse is repaired and the bladder neck is reinforced. The operation is performed vaginally. It is an old operation and it is mentioned here be mainly because of its popularity. However, its success rate is poor and in the order of 50-60%. It is perhaps useful only to repair the prolapse but certainly not ideal for correcting incontinence.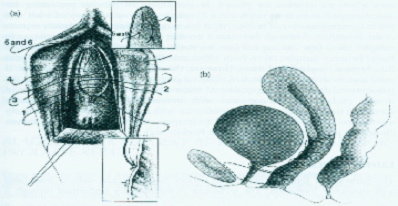
Sub-urethral slings
Through a big incision in the abdominal wall strong tissue is obtained from it and it is placed under the bladder neck to elevate it. The sling tissue is stitched back to the abdominal wall.
Tension Free tape Procedure
A synthetic tape or mesh is placed underneath the middle section of the outlet (urethra) under no tension. This is tunneled behind the pubic bone to just under the abdominal wall or the labial skin. These operations appear to have a high success rate comparable to the Burch procedure.

Peri-urethral injections
A bulking agent or implant is injected into the tissues around the urethra to partially close it. It may be used in patients where a sling fails to provide full cure. The succes rate is only moderate but it avoids open surgery.

Open Burch colposuspension
This operation involves a big cut of 10-12 cm across the lower abdomen. It elevates the bladder neck back to its normal position. It is considered one of the best operations for stress incontinence with a success rate of 90%. It avoids also the use of mesh.
Laparoscopic Burch colposuspension
Gynaecologists with special training in advanced laparoscopic surgery may perform the Burch colposuspension through “key-hole” surgery, using only 4 small 5-10 mm incisions in the abdominal wall. It results in less postoperative pain with a quicker return to normal activities. It provides also with an opportunity to assess your pelvis and avoids the use of mesh.
For more information, please contact us